Losing your hair can be emotionally challenging. If you’re one of the millions of people worldwide affected by hair loss, you’ve likely spent hours searching for solutions. While surgical hair transplants are a permanent option, many people prefer to start with less invasive, more flexible choices. The solution for many lies in the powerful and continuously evolving field of non-surgical hair restoration.
This ultimate guide to the Nova Voya Platform will take you through every major non-surgical hair restoration method, from cutting-edge regenerative therapies like Exosomes to tried-and-true medications. We’ll break down the real costs, compare the long-term effectiveness, and give you a simple framework for choosing the right treatment plan for your hair loss journey.
Key Takeaways: What You’ll Learn
- Non-Surgical Treatments Work: Methods like PRP, Minoxidil, and Finasteride effectively slow hair loss and promote regrowth, but they require consistent, long-term maintenance.
- Cost is Cumulative: Initial costs are low, but the total 5- to 10-year investment can equal or exceed a one-time surgical transplant cost. Budget for maintenance.
- Combination is King: The best results are achieved by stacking treatments (e.g., combining a DHT blocker like Finasteride with a Stimulator like Minoxidil or PRP).
- Start Early: Treating hair loss in the early stages (Norwood 1-3 or Ludwig I-II) yields the most dramatic and lasting results.
- Gender Matters: Women’s hair loss is often rooted in stress and hormones; treatment protocols must be tailored to address these unique triggers.
What Is Non-Surgical Hair Restoration? (Definition & Overview)
Let’s start by understanding what non-surgical hair restoration actually is and how it differs from permanent surgical solutions.
Non-surgical hair restoration refers to any treatment designed to slow hair loss, stimulate new hair growth, or improve the appearance of hair density without the need for invasive surgical procedures like Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) or Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT).
These treatments focus primarily on creating a healthier environment for existing hair follicles, stopping the root causes of miniaturization (the shrinking of the follicle), and promoting the shift of dormant hairs into the active growth (anagen) phase. For many seeking non-invasive hair loss treatment, these methods offer a fantastic starting point.
How Non-Surgical Hair Restoration Works
Non-surgical methods address the core biological and physiological factors that lead to hair thinning. The mechanisms vary widely by treatment, but they generally fall into three categories: Follicle Stimulation (PRP, LLLT), Hormonal Regulation (Finasteride), and Cosmetic Density (SMP).
Who Is a Good Candidate for Non-Surgical Treatments?
If you are experiencing mild to moderate hair thinning, you are likely an excellent candidate for non-surgical hair restoration. These treatments work best when the hair follicle is still alive and responsive, even if it has shrunk (miniaturized). Candidates include early-stage hair loss sufferers, those hesitant about surgery, women, and individuals preparing for future hair transplants.
Key Differences Between Non-Surgical and Surgical Hair Restoration
| Feature | Non-Surgical Hair Restoration | Surgical Hair Restoration (FUE/FUT) |
| Invasiveness | Non-invasive or minimally invasive (e.g., injections) | Invasive; requires surgical incisions |
| Downtime | Minimal to none (minutes to a few hours) | Days to a week or more |
| Permanence | Requires ongoing maintenance to sustain results | Considered permanent (grafted hairs are resistant to loss) |
| Cost | Lower initial cost, but high cumulative long-term cost | High upfront cost, low long-term maintenance cost |
| Mechanism | Stimulates existing follicles, prevents loss, improves appearance | Relocates healthy follicles from one area to another |
The Science Behind Hair Loss: Understanding Your Problem
Before exploring treatment options, it’s important to understand why hair loss happens in the first place. This knowledge is key to finding the right hair restoration without surgery.
Hair loss, or alopecia, is typically categorized by the cause. Understanding your specific type of hair loss is the first step toward effective treatment.
Male Pattern Hair Loss (Androgenetic Alopecia)
This is the most common cause of hair loss, affecting up to 50% of men by age 50. It’s primarily driven by genetics and hormones. Androgenetic alopecia occurs when hair follicles have a genetic sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT binds to receptors, causing follicle miniaturization, where the follicle gradually shrinks, producing shorter, thinner hairs until it stops altogether. In men, this loss follows a predictable pattern: a receding hairline and thinning on the crown (Norwood Scale).
Female Pattern Hair Loss and Gender-Specific Causes
Female pattern hair loss (FPHL) affects millions of women. Unlike men, women rarely go completely bald; they typically experience diffuse thinning across the entire scalp (Ludwig Scale). FPHL is often influenced by hormonal shifts (menopause, PCOS), stress-induced hair shedding (Telogen Effluvium), thyroid issues, and nutritional deficiencies. Recent data shows a concerning trend: women aged 18-65 are now reporting thinning hair more often than men in the same age group.
Other Types of Hair Loss: Stress, Hormonal, and Medical Triggers
Not all hair loss is permanent or genetic. Telogen Effluvium is a temporary shedding triggered by severe stress, surgery, or childbirth. Hormonal imbalances, such as those related to thyroid function, can also trigger hair loss. Finally, certain medications and deficiencies (especially Iron, Zinc, and Vitamin D) can be underlying causes that must be medically addressed before any treatment can succeed.
The Role of Genetics: Why Some People Are More Prone to Hair Loss
Genetics is the primary determinant of who will experience pattern hair loss and how severe it will be. While genetics sets the potential due to DHT sensitivity, lifestyle, diet, and stress are environmental factors that influence the timing and severity. Early intervention using hair restoration without surgery can dramatically slow or stop the progression.
Top Non-Surgical Hair Restoration Methods Explained
Here are the most effective non-surgical options, each with unique mechanisms and results. This is the heart of finding the best hair loss treatment without surgery.
1. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP is a leading PRP hair restoration method that uses your body’s own biology to stimulate hair growth. It involves drawing blood, processing it in a centrifuge to isolate concentrated platelets, and injecting the resulting platelet-rich plasma into the thinning areas of the scalp. These growth factors stimulate follicle stem cells, prolong the active growth (anagen) phase, and improve blood flow, slowing miniaturization.
- Treatment Schedule: Patients need an initial series of 3 to 4 treatments (4-6 weeks apart), followed by maintenance injections every 6 to 12 months.
- Cost & Timeline: Initial costs range from $500 to $1,500 per session. Visible results are achieved over 6–12 months. Clinical studies confirm PRP can significantly increase hair density, averaging 14 to 45 hairs per cm² in treated areas ([Source: National Institutes of Health, NCBI]).
2. Oral and Topical Medications (Finasteride & Minoxidil)
Pharmaceuticals are often the most reliable and budget-friendly form of non-surgical hair restoration.
- Finasteride (Propecia): An oral medication primarily for men, it works by blocking the enzyme that converts testosterone into hair-damaging DHT, thereby stopping follicle miniaturization. It prevents hair loss progression in over 80% of men.
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): An over-the-counter topical solution or foam for both men and women. It improves scalp circulation and shifts hairs into the active growth phase. It promotes hair regrowth in 30% to 50% of users. Topical Minoxidil is the only FDA-approved non-surgical hair restoration method for women.
- Combination Therapy: Combining Finasteride (hormonal block) and Minoxidil (stimulation) is highly recommended for synergistic, superior results.
3. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) and Red Light Devices
LLLT uses specific wavelengths of non-heating light energy, delivered via helmets or caps (Red Light Therapy), to stimulate cellular function in the scalp. The energy is absorbed by follicle cells, increasing their metabolic rate, prolonging the anagen phase, and promoting hair thickening.
- Usage: Devices are available for convenient at-home use or in-office treatments.
- Results: Consistency is vital, requiring daily or near-daily use (20-30 minutes). Visible density improvements typically appear around the 6-month mark. LLLT is considered one of the safest treatment options available.
4. Exosome Therapy: The Newest Regenerative Option
Exosome therapy is the cutting edge of regenerative non-surgical hair restoration. Exosomes are tiny, nano-sized vesicles released by stem cells that act as concentrated messengers, delivering potent signaling molecules directly to dormant hair follicles. This instructs them to regenerate and re-enter the active growth phase, offering a more concentrated and potentially powerful treatment than PRP. Exosome therapy is currently in the premium cost bracket.
5. TransEpidermal Delivery (TED) and Micro-Channeling
This technology focuses on bypassing the skin’s barrier. TED uses acoustic sound waves and air pressure to temporarily open micro-channels in the scalp, allowing specialized, powerful serums (peptides, growth factors) to be pushed deep into the hair follicles where they can be fully absorbed. TED is most effective when combined with other active treatments like serums or post-PRP.
6. Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP): The Illusion of Density
SMP is a specialized cosmetic tattooing technique that offers an immediate, visually powerful solution for advanced thinning or baldness. It involves tattooing tiny pigment dots onto the scalp, mimicking the appearance of shaven hair follicles. This creates the look of a full, closely-shaved head or reduces the contrast between existing hair and scalp for greater visual density. SMP is semi-permanent and lasts 4 to 6 years before a touch-up is needed.
7. Hair Growth Serums and Nutraceutical Supplements
High-quality serums and supplements support hair health but do not replace clinical treatments. Medical-grade serums contain proven active ingredients like peptides, while nutraceuticals focus on correcting nutritional deficiencies. Key micronutrients for hair health include Zinc, Iron (Ferritin), Biotin, and Vitamin D. Supplements should only be taken after confirming a deficiency via a blood test.
8. Hair Systems and Modern Hair Prosthetics
For individuals with advanced hair loss (Norwood 5+ or Ludwig III) who prefer immediate, guaranteed density, modern hair systems (wigs or pieces) offer a realistic solution. Custom systems match the user’s hair and scalp contour. They require professional maintenance every 3 to 6 weeks and last 6 to 12 months before replacement.
Non-Surgical Hair Restoration Cost Breakdown
Understanding the financial investment required is crucial when deciding on a treatment plan.
Initial Treatment Costs by Method
| Treatment Method | Initial Cost per Treatment/Month | Frequency |
| Oral/Topical Meds (Minoxidil/Finasteride) | $20 – $80/month | Daily |
| LLLT At-Home Device | $300 – $1,500 (one-time purchase) | Daily/Weekly |
| PRP Therapy | $500 – $1,500 per session | 3-4 initial, then 1-2 per year |
| Exosome Therapy | $2,000 – $5,000 per session | Highly variable, often 1-2 per year |
| Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP) | $2,500 – $4,500 (full treatment) | 1-3 sessions, touch-up every 4-6 years |
| Hair Systems | $500 – $1,200 per unit + $150/month maintenance | Replacement every 6-12 months |
Long-Term Maintenance Costs and Hidden Expenses
The real cost of non-surgical hair restoration lies in its continuity. Non-surgical treatments require ongoing monthly or annual investment to sustain the results.
Cumulative 5-Year and 10-Year Cost Projections
This long-term analysis is critical for the cost-conscious evaluator. The ongoing nature of maintenance means that the total cumulative cost over 5 to 10 years can often match or exceed the high upfront price of a single hair transplant.
Effectiveness and Results: What the Research Shows
Scientific evidence is essential for evaluating which treatments actually deliver measurable results. We focus on evidence-based hair restoration methods for men and women.
PRP, Medication, and LLLT Effectiveness
- PRP Success: Clinical studies show PRP can significantly increase hair density, with results often ranging from 14 to 45 hairs per cm² in treated areas.
- Medication Efficacy: Finasteride stops hair loss progression in over 80% of men. Minoxidil promotes hair regrowth in 30% to 50% of users (both men and women).
- Combination Therapy: The combination of Finasteride (DHT block) and Minoxidil (stimulation) yields superior results.
- LLLT Evidence: Clinical trials demonstrate LLLT can increase hair thickness and improve overall density, provided the treatment is used consistently for 3-4 months.
Realistic Expectations: Before and After Timelines
Setting realistic expectations is crucial, as no treatment works overnight.
- Early Results (1-3 Months): Expect increased shedding (temporary Minoxidil/PRP effect) and reduced oiliness. True growth takes time.
- Intermediate Improvements (3-6 Months): Noticeable decrease in shedding. Hairs may feel thicker, and minimal visual changes in density may be visible.
- Optimal Results (6-12 Months): Significant visual improvements in hair density, thickness, and coverage are evident.
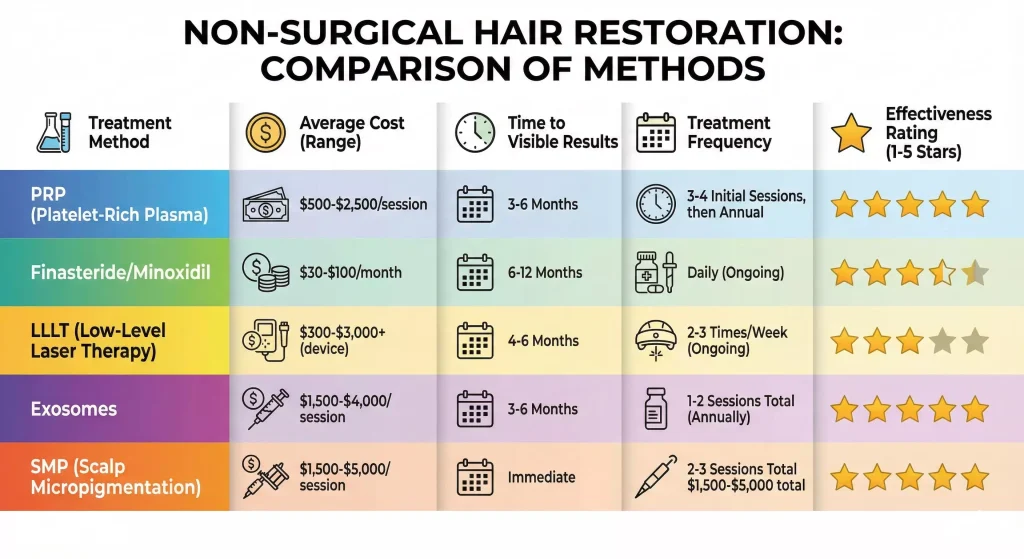
Comparing Treatment Methods: A Side-by-Side Analysis
To help you decide, here’s how the major non-surgical options stack up against each other.
Comparison Table: Cost, Downtime, Results, and Maintenance
Which Treatment Is Best for Different Hair Loss Stages?
The best approach depends on the severity of your hair loss.
- Early Stage (Stages 1–2): Focus on prevention: Topical Minoxidil, oral Finasteride (men), and LLLT.
- Moderate Hair Loss (Stages 3–4): Use a regenerative approach: Combination therapy (Meds + LLLT) and Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) or Exosome Therapy.
- Advanced Hair Loss (Stages 5–6): Focus on maximizing remaining density or utilizing cosmetic alternatives like Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP) or hair systems.
Combining Multiple Treatments for Maximum Results
Layering treatments (stacking approaches) is the most effective way to fight hair loss. The best protocols typically combine a DHT blocker (like Finasteride) with a Stimulator (like Minoxidil or LLLT) and an Accelerator (like PRP or Exosomes). This addresses multiple biological pathways for superior outcomes.
Gender-Specific Considerations: Men vs. Women
Hair loss affects men and women differently, and treatment must be tailored.
The Best Non-Surgical Options for Men
Male hair loss is aggressive due to DHT. The cornerstone of male treatment is combining Finasteride (blocks DHT) with Minoxidil (stimulates growth). Regenerative therapies like PRP also work well, particularly when used alongside Finasteride.
Non-Surgical Hair Restoration for Women
Female pattern hair loss is complex, often driven by stress, hormones, and deficiencies.
- Safe Options: Minoxidil (FDA-approved), PRP, and LLLT are safe and effective.
- Root Cause: Treatments for women must often address the root cause, such as managing stress, optimizing thyroid function, and correcting Iron Deficiency.
- Avoid: Oral Finasteride is usually avoided in women of childbearing age.
Side Effects and Safety: What You Need to Know
Understanding potential risks is important for informed decision-making ([Source: Harvard Health]).
Safety Profile by Treatment
- PRP and Exosome Therapy: Considered extremely safe (autologous treatment), with minimal risks like temporary swelling or bruising at injection sites.
- Minoxidil: Common side effects include temporary scalp irritation or increased initial shedding.
- Finasteride: Generally well-tolerated, but carries a small risk (around 1-2%) of sexual dysfunction, which is often reversible. LLLT has no reported permanent adverse effects.
Creating a Personalized Safety Plan with Your Provider
The best way to manage side effects is to consult with a dermatologist or hair specialist who can review your full medical history and design a personalized safety plan.
Lifestyle and Prevention: Maximizing Treatment Results
Lifestyle changes significantly enhance treatment outcomes.
Key Lifestyle Pillars
- Managing Stress: Chronic high stress increases cortisol, causing shedding (Telogen Effluvium). Implement stress management techniques (mindfulness, exercise) to support a healthy hair growth cycle.
- Nutritional Support: Ensure optimal levels of key nutrients like Zinc, Iron, Biotin, and Vitamin D. Supplements should only be taken if a deficiency is confirmed.
- Hair Care Best Practices: Avoid tight hairstyles that cause Traction Alopecia. Use mild shampoos and minimize the use of high-heat styling tools to prevent breakage.
- Medical Conditions: Underlying issues like Thyroid Dysfunction or Iron Deficiency must be corrected, as they directly trigger hair loss.
Choosing the Right Treatment: A Decision Framework
Use this framework to identify the best treatment plan for your specific situation.
- Step 1: Assess Your Hair Loss Stage and Severity (Norwood/Ludwig scale).
- Step 2: Evaluate Your Budget and Timeline (Consider the cumulative 5-year cost vs. upfront costs).
- Step 3: Consider Your Lifestyle and Commitment Level (Consistency is the key to success).
- Step 4: Consult with a Dermatologist or Hair Specialist (For customized testing and combination therapy design).
How to Prepare for Your First Consultation
Bring a list of medications, recent blood test results, and photos showing your hair loss progression to your consultation.
Summary and Conclusion
Here’s what every person considering non-surgical hair restoration should remember.
The landscape of hair loss treatment has never been more advanced. You have incredible options, from life-changing medications to regenerative therapies that harness your body’s own power to regrow hair. The core truth is this: the sooner you start, the better your results will be. Non-surgical hair restoration is a journey, not a destination, and consistency with your chosen protocol is the key to maintaining your hair health for years to come.
- Actionable Insight: The cumulative cost of non-surgical treatments over 5 to 10 years can equal or exceed the cost of a hair transplant. Plan your budget for the long term.
- The Power of Combination: Stacking approaches (e.g., Minoxidil + PRP) yields superior results because you attack hair loss from multiple biological angles.
- Personalization is Key: Always consult with a specialist for blood tests and a personalized protocol, especially women, whose hair loss is often rooted in stress and hormones.
When to seek professional help: If you notice any sudden, rapid hair loss, significant widening of your hair part, or if you feel severe emotional distress over your thinning hair, it’s time to see a specialist.
Next steps for taking action: Start by assessing your hair loss stage and researching clinics that offer the treatments you are most interested in, such as PRP or Exosome therapy.
Ready to stop searching and start growing?
Nova Voya is an extensive collaboration platform built with a network of top clinics, hospitals, and specialized physicians across various therapeutic fields.
The platform offers exclusive discounts and unique deals, allowing you to access quality hair loss treatments, particularly focusing on non-surgical and advanced procedures.
Schedule a free, personalized consultation with the hair restoration experts today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, it works. Clinical studies show PRP increases density (14-45 hairs per cm²), and minoxidil/finasteride can regrow hair in 30-50% of users. Success requires starting early and maintaining consistency.
Timelines vary: Minoxidil/Finasteride usually shows results in 3-6 months. PRP and LLLT show improvements over 6-12 months. Ongoing maintenance is required for all methods to sustain results.
Combining treatments often yields superior results. Common combinations include Minoxidil + Finasteride, PRP + medications, or laser therapy + serums. Consult your dermatologist for a customized protocol.
Minoxidil is FDA-approved and effective for women. PRP and Red Light Therapy are also safe and popular. Finasteride is NOT approved for women. Treatment must address hormonal and nutritional root causes specific to women’s hair loss.
Non-surgical options are cheaper initially ($20-$1,500 per month/session). However, the cumulative cost over 5-10 years can match or exceed the $8,000-$15,000 one-time cost of a transplant because non-surgical methods require ongoing maintenance.
Yes. Non-surgical treatments can actually improve hair transplant outcomes when used beforehand. Starting treatments early maximizes future options, even if a transplant is eventually needed.
PRP for hair restoration is typically considered cosmetic and is NOT covered by insurance. Most treatments are out-of-pocket expenses.
Most treatments have minimal, temporary side effects (e.g., Minoxidil irritation, temporary shedding). PRP/Exosome risks are low. Finasteride carries a small risk of reversible sexual dysfunction. LLLT has no reported permanent adverse effects.